The Good Ventures Circular Business Opportunity Flywheel provides a comprehensive framework for businesses to understand and assess their opportunities of implementing circular economy practices into their core operations.
The Circular Business Opportunity Flywheel
> Circular design and production
Circular design and production envision the complete lifespan of products, focusing on durability, repairability, and recyclability as well as efficient and sustainable use of raw materials. These practices help companies reduce virgin material usage and create products that can be easily disassembled and repaired for reuse. Designing products that are built to last and are easily updated or refurbished allows companies to offer lifecycle services and create recommerce business, generating ongoing revenue.
When focusing on sustainable production practices, companies can find opportunities to utilize or monetize side streams from own production or benefiting from other companies’ side streams.
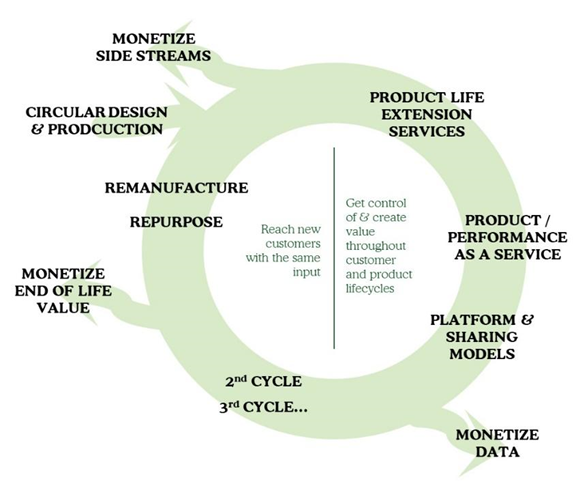
Circular business opportunity flywheel is a strategic framework for identifying and capitalizing on circular economy opportunities. (Copyright Good Ventures)
> Product life extension services
Extending the lifecycle of products through maintenance, repairs, and upgrades is a core aspect of the circular economy. Lifetime guarantees and predictive maintenance optimize operations, reduce downtime, and enhance customer satisfaction. Remanufacturing services further extend product lifetimes by restoring used products to like-new condition. These capabilities enable the next steps along the flywheel.
> Product / performance as a service
To capture the value of longer lifespan, companies need to develop new business models. For example, shifting from ownership to a service-based model where customers pay for performance, or the use of a product maximizes value throughout the product’s lifecycle. This model incentivizes companies to design durable, high-quality products and fosters ongoing customer interaction, increasing loyalty and cross-selling opportunities. In addition, PaaS business models eliminate the need for large upfront investments from customers, creating new growth opportunities for sellers. These models require a new approach to and structure of business.
> Platform and sharing models
Collaborative consumption, or sharing models significantly reduce material inefficiencies by promoting sharing of resources and peer-to-peer exchanges. Platform, sharing and rental business models increase asset utilization, reduce the need for new resources, and create new revenue streams and business opportunities.
> Monetize data
The use of data to optimize operations and create new revenue streams is a powerful tool in the circular economy. By leveraging IoT and advanced analytics, companies can gain insights into product usage and condition. This insight can then be turned into new or improved services. Data-driven approaches enable businesses to optimize their operations and those of their customers, enhancing the overall customer experience and creating new revenue opportunities – or even new business areas.
> Second cycle
Building second cycle operations and capabilities allows products to re-enter the market multiple times. Additional cycles involve refurbishing and reselling used products, providing customers with high-quality, affordable options and extending the product’s lifecycle. Take-back programs allow customers to return used products for incentives. These items can be refurbished or repaired and resold at lower prices, reducing waste, raw material demand, and offering affordable, environmentally friendly products to existing or new markets.
> Repurpose / Remanufacturing
Recovery schemes for end-of-life products capture significant value by presenting the opportunity to utilize valuable components and raw material further. Remanufacturing restores used products to like-new condition, while repurposing finds new uses for old products, components or materials.
Recycling and upcycling ensure continuous re-entry of materials into the value chain, transforming waste into new products and reducing landfill use. With scarce materials, there is a significant potential in monetizing end-of-life value. These practices reduce waste, conserve energy and resources, and lead to cost savings for both companies and customers.
+ How are Finnish companies embracing biodiversity opportunities?

Designing products that are built to last and are easily updated or refurbished allows companies to offer lifecycle services and create recommerce business, generating ongoing revenue.
>> Good Ventures: Circular business whitepaper
Sounds easy? We know it isn’t. Many times, it seems easier to continue with the linear business models. However, the business opportunities presented above are not just future opportunities, they might be solutions to the pressing problems of today. To further illustrate this, we present in our Circular business whitepaper real-world case studies, focusing on high price-point product business, showcasing how industry leaders are implementing circular practices. By examining examples, decision-makers can gain valuable insights into the practical application of circular economy principles and how to apply similar principles into their own businesses.
Circular economy is the best available solution for businesses to combat climate crisis and biodiversity loss. In addition, it is already the greatest business opportunity of our time! Good Ventures is publishing a practical model and several interesting case examples to help companies identify their circular business opportunities and adopt circular business models step by step to create sustainable growth. Read the whitepaper here (Good Ventures)
Palaa etusivulle


